In modern industry, healthcare, office, and smart home sectors, the demand for vertical lifting is growing. From desks and electric lecterns to nursing beds, operating tables, and even liftable TV cabinets and kitchen countertops, stable, high-precision, and low-noise lifting devices have become core hardware. Lifting columns, as multi-stage telescopic lifting devices integrating motors, guide rails, linear actuators, and control systems, are gaining widespread application across various industries due to their compact structure, high load-bearing capacity, and smooth lifting characteristics. This guide will detail the definition, composition, working principle, application areas, advantages and limitations, selection and maintenance methods, and future market trends of lifting columns, providing readers with a comprehensive reference.
1. What is a Lifting Column?
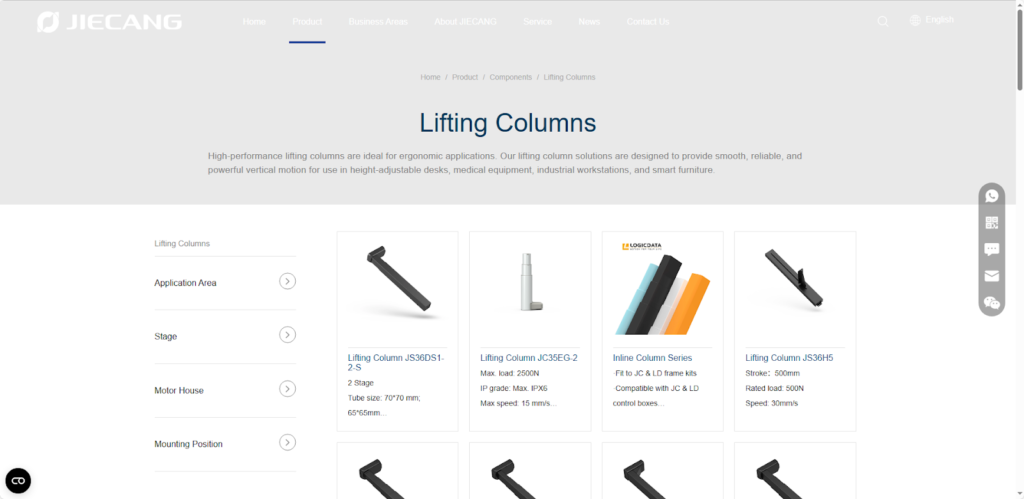
A rising column is a multi-stage telescopic lifting device that integrates a linear actuator, guide mechanism, and structural support. Its compact structure allows for high-precision height adjustment within limited space, resulting in a stable and tidy system.
Rising columns have a wide range of applications, especially suitable for scenarios requiring precise vertical lifting. For example, in industrial automation, they can be used as height adjustment platforms on assembly lines; in medical equipment, they can support imaging equipment, nursing beds, or operating tables, enabling smooth and safe lifting; and in smart office furniture, they can be used in electric height-adjustable desks, display shelves, or television lifting systems, making daily life and work more comfortable and efficient. Whether in terms of high load capacity, high precision, or low-noise operation, rising columns exhibit advantages unmatched by traditional mechanical or single-stage actuators.
2. Working Principle of Lifting Columns
The core operating principle of lifting columns is based on a motor-driven lead screw.When the motor starts, the lead screw rotates slowly, precisely pushing each telescopic section up and down under the guidance of guide rails and sliders, ensuring a smooth lifting process without rotational deviation. The multi-stage telescopic design allows the lifting column to achieve a large stroke within a limited space while maintaining high stability and load-bearing capacity.
To achieve precise control, modern lifting columns are typically equipped with built-in sensors, such as Hall effect sensors or other position feedback devices. These sensors monitor the position of each telescopic section in real time, transmitting the data back to the controller for highly precise lifting operations. Combined with the control system, the lifting column can perform various intelligent functions, such as synchronous lifting, preset height memory, and travel limit protection, ensuring both safety and efficiency during use.
Furthermore, the guide rail and slider system plays a crucial role throughout the entire movement process. It not only ensures the synchronous movement of the multi-stage structure but also prevents lateral twisting or swaying that may occur during lifting, ensuring the equipment remains stable and reliable even when carrying heavy loads. Combining precision motors, intelligent sensors, and stable guide rails, the rising column can provide a precise, low-noise, and controllable vertical lifting experience in various scenarios such as industry, medical care, and furniture, meeting the requirements of high load, high precision, and safety.
3. Advantages of Lifting Columns
Lifting columns offer significant advantages over traditional electric linear actuators. Firstly, they offer greater stability. The multi-stage telescopic structure combined with a guide rail system minimizes lateral forces during lifting, ensuring stability when carrying loads and preventing swaying or tilting. Aesthetically, lifting columns are typically fully enclosed, with clean, sleek lines that blend seamlessly with equipment or furniture designs, unlike the overly mechanical appearance of exposed linear actuators.
Low noise levels are another major advantage. High-precision motors and guide rail systems ensure smooth and quiet operation, making them suitable for demanding environments such as offices, medical facilities, or homes. Multi-column systems (typically 2–4 columns) enable precise synchronous lifting, providing reliable support for high-repetition, high-precision applications. Furthermore, lifting columns are easily integrated with control systems, including switches, buttons, PLCs, or intelligent control modules, supporting features such as height memory, limit protection, and multi-column联动 control, making operation more flexible, safe, and efficient.
Conclusion
In modern industry, healthcare, office, and smart home sectors, rising columns have become the core hardware of vertical lifting systems due to their compact structure, high load-bearing capacity, smooth lifting, and low noise. Whether it’s an office desk, electric lectern, nursing bed, operating table, or even a height-adjustable TV cabinet and kitchen countertop, rising columns provide precise, efficient, and reliable height adjustment. Through proper selection, correct installation, and regular maintenance, rising columns not only improve operational convenience and lifespan but also bring users a more comfortable, safe, and intelligent user experience. With the development of intelligent control, IoT integration, and multi-column synchronization technology, rising columns will continue to expand their application scenarios in the future, becoming standard equipment in high-end lifting solutions.
Lifting Column FAQ
1. What is a Lifting Column?
A lifting column is a multi-stage telescopic lifting device integrating a motor, guide rails, linear actuators, and a control system, enabling smooth and precise vertical lifting. It is widely used in office furniture, medical equipment, industrial automation, and smart home applications.
2. What are the core components of a lifting column?
These mainly include: a multi-stage telescopic structure (typically 2-3 sections), a built-in electric linear actuator, a guide rail system, a motor (DC/AC), a control system (switch, button, PLC, or wireless), safety devices (anti-pinch, overload protection), and an aluminum or steel body. Each component affects the stability, load-bearing capacity, and lifespan of the lifting column.
3. How does a lifting column work?
The motor drives a lead screw to produce linear motion, causing the multi-section structure to extend or retract sequentially. The guide rails and sliders ensure smooth lifting without rotation, and built-in sensors (Hall sensors or position feedback) achieve precise height control. The controller can support multi-column synchronization, height memory, and travel limit functions.